The main authors of this paper are not the same as DINO. This paper is more like ConvNext, where we just keep stacking techniques. A better name of the paper is “better iBOT”.
Data processing
We assemble our curated LVD-142M dataset by retrieving, from a large pool of uncurated data, images that are close to those in several curated datasets dino_v2, page 4
- SSCD is used to remove duplicate images.
- Retrieve images from uncurated data source that’s close to curated sources. With a self-supervised ViT(not sure what exactly, not important), compute similarity with cosine image embedding, Then do k-means. If the cluster (?) is large, get 4 neighbors, else just sample from the cluster.
- Faiss is used for large scale similarity search.
The model
A conglomeration of these:
- Image level objective. This is the loss from DINO, the cross entropy loss between teacher and student.
- Patch-level objective. This one is from iBOT.
- Untying head weights. iBOT paper share the parameter for the MLP projection head for the losses. This does not.
- Sinkhorn-Knopp centering. This type of batch normalization is adapted from SwAV
- KoLeo regularizer. This is a regularization term that encourage a uniform span of the features within a batch.
- During a short period at the end of pretraining, use a higher resolution of images (518x518). That’s because training at high resolution throughout the training is time and memory demanding.
Efficient implementation
- FlashAttention is used. Now we have v2 though.
- Sequence packing. DINO forwards both large and small crops. To forward them together, concat all the sequence into a single long sequence, then use block-diagonal mask to prevent attention between different sequences. The implementation is in xFormers library.
- Efficient stochastic depth. For that work, “we start with very deep networks but during training, for each mini-batch, randomly drop a subset of layers and bypass them with the identity function.” In this work, we “skip the computation of the dropped residuals rather than masking the result” to make it more efficient.
- Fully-Shared Data Parallel. The better DDP.
- Knowledge Distilling: the smaller model of this paper is got by distilling instead of training from scratch.
we use a larger model as a frozen teacher, keep a spare EMA of the student that we use as our final model, remove the masking and stochastic depth, and, apply the iBOT loss on the two global crops. dino_v2, page 7
Ablation
Training recipe
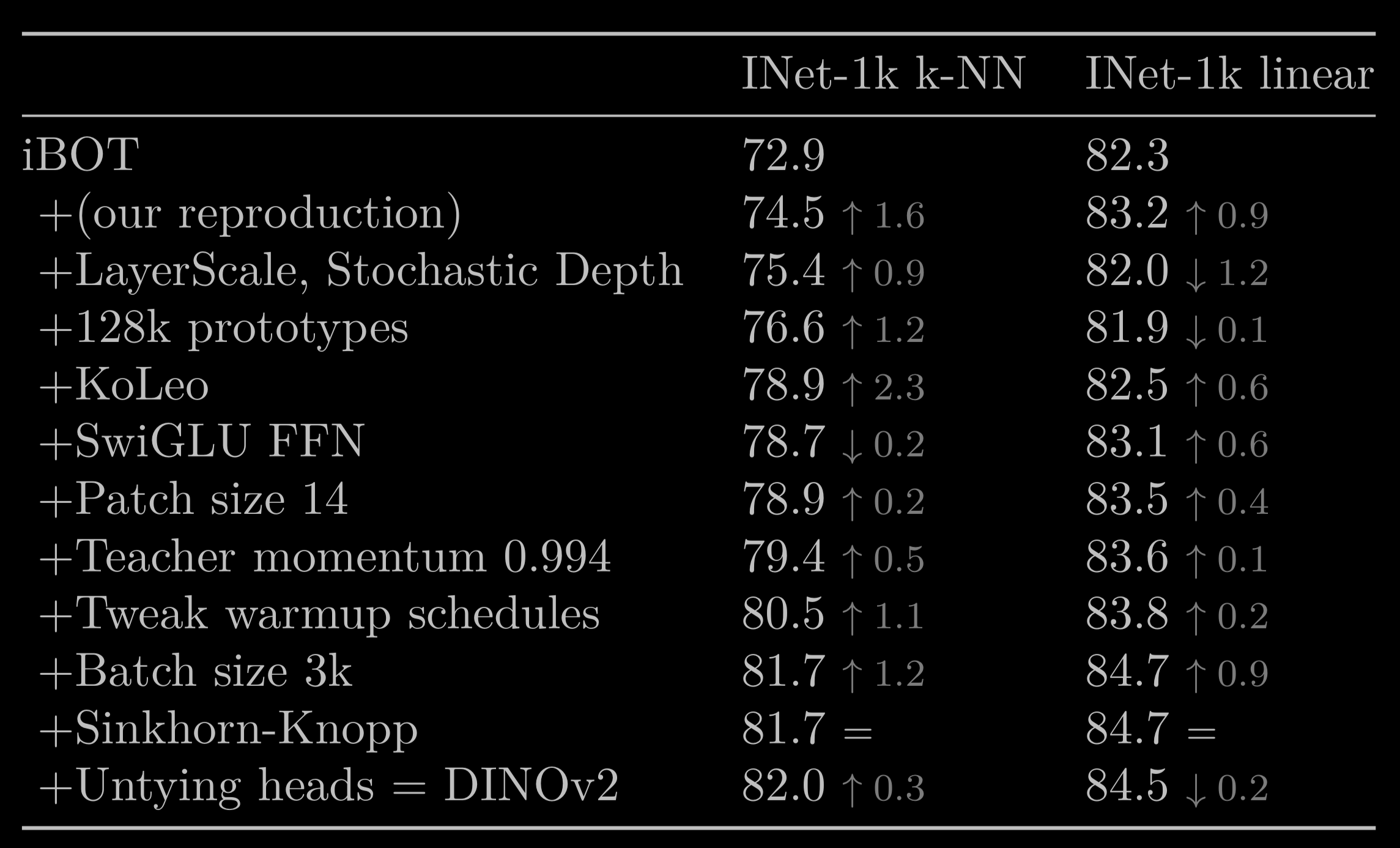 This table is very much like the one for ConvNext.
This table is very much like the one for ConvNext.
Pretraining data source
The curated LVD-124M is just slightly better than raw INet-22k.