I’m so disappointed In the HuggingFace online course, I would start my notes from scratch with DeepMind x UCL 2021 lecture series.
The why
The reward hypothesis:
Any goal can be formalized as the outcome of maximizing a communal award reward.
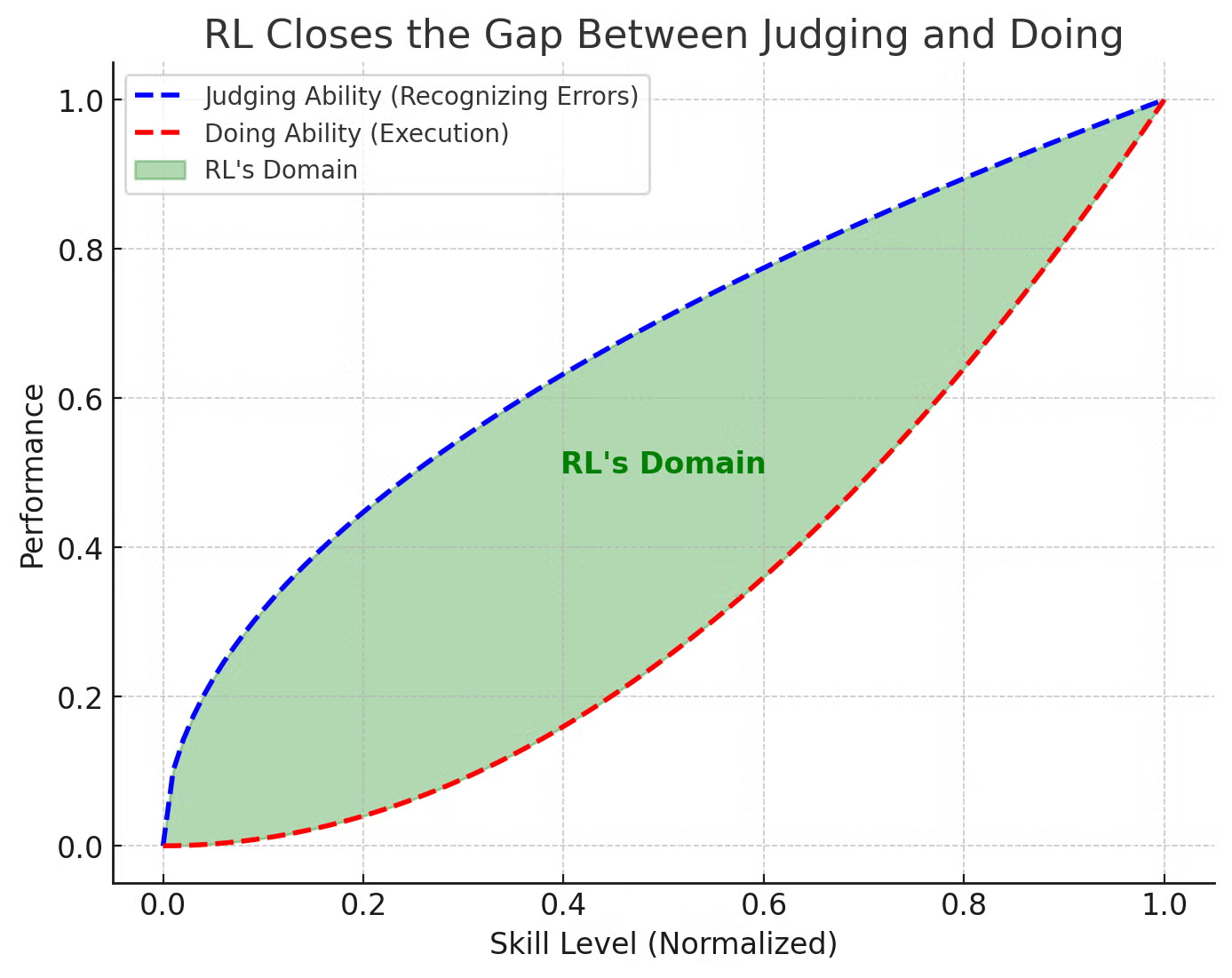
I would also like to put this image here from LLM Post-Training that I find helpful:
State
As we can see from control theory, the definition of state can be crucial. There are environment state and agent state. Let’s talk about agent state here. The history is
The markovian agent state typically is some compression of . The full hitory is Markov (but keeps growing). In an environment with partial observability, the observations are not Markovian, making them a POMDP. The environment state may still be Markovian, but the agent does not know it.
Value function
A quick reminder: we need the notion of value / state, since the reward only have meaning in a state. It’s in a specific state that we receives reward, not with a specific action. In other words, state is how we define the state where we could get reward.
The actual value function is defined as
means we only care about the instant reward, while means it considers long term and immediate rewards equally. Personally I’m interested to see if there are alternative definitions. There’s no reason it’s defined like this.
The bellman equation is its recursive form, the Bellman equation.
Now note here that is chosen by policy in state . We can take out the dependency on a specific policy by stating that the following holds for the optimal case:
model
A model predicts what the environment will do next. It can predict the next state, or the next (immediate reward). Note it does not directly give a policy.
Prediction and control
This is like the Expecation-maximization algorithm.
- Prediction: evaluate the future (for a given policy)
- Control: optimise the future (find the best policy)
Info
The rest of the note comes from 285-rl-basics.pdf
In RL, we almost always care about expectation since that makes things smooth. - not smooth - smooth in
The slide also gives good explanation to algorithm tradeoffs, why we need different kind of them, etc.